Radiofrecuencia de tumores renales:
10 años de experiencia
Palabras clave:
tumor renal, tumores renales, Radiofrecuencia, poster, seramResumen
Objetivos
La mayoría de tumores renales se diagnostican de forma incidental en estudios radiológicos. Entre el 70-80% de los incidentalomas se hallan en fase precoz no metastásica.
La nefrectomía parcial es el tratamiento de elección en estos pacientes, aunque las guías de la Asociación Amerciana de Urología (AUA) ya recomiendan el tratamiento ablativo en tumores en estadio T1a (<4cm).
Las indicaciones incluyen los pacientes que son pobres candidatos a cirugía o bien aquellos con tumores múltiples.
La eficacia de la radiofrecuencia renal (RF) es equiparable a la de la cirugía conservadora a corto y medio plazo.
El objetivo de este estudio es evaluar la eficacia y seguridad de la RF con intención curativa en pacientes de alto riesgo con un seguimiento a medio plazo a lo largo de un periodo de 10 años.
Material y métodos
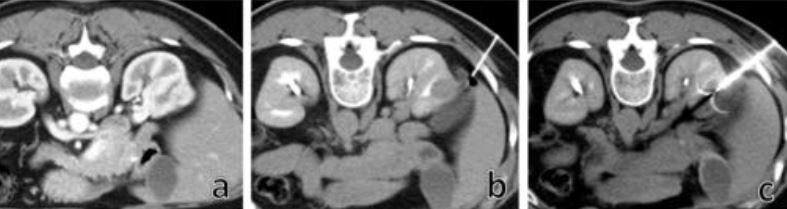
Se trata de un estudio retrospectivo realizado en 87 pacientes (59 hombres y 28 mujeres con una media de edad de 73,7 años, desviación estándar de 10,87) y 89 nódulos, con pacientes propios del centro (n=57) y derivados de otros 4 centros de Catalunya (n=30,) entre noviembre de 2005 y mayo de 2015, que presentaban tumores en estadíos T1a y T1b. Se excluyeron del estudio los nódulos tratados mediante microondas (n=2) y los que se sometieron a RF y embolización (n=1). La mayoría de los pacientes tratados tenían un riesgo quirúrgico alto o muy alto (Índice ASA de la Sociedad Americana de Anestesiología III o IV). Las características de los pacientes y de los tumores se detallan en la tabla 1.
Descargas
Citas
- Chow WH, Devesa SS, Warren JL, Fraumeni JF. Rising incidence of renal cell cancer in the United States. JAMA [Internet]. 1999 May 5 [cited 2015 Oct 13];281(17):1628–31. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10235157
- Homma Y, Kawabe K, Kitamura T, Nishimura Y, Shinohara M, Kondo Y, et al. Increased incidental detection and reduced mortality in renal cancer--recent retrospective analysis at eight institutions. Int J Urol [Internet]. 1995 May [cited 2015 Oct 26];2(2):77–80. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7553292
- Simard EP, Ward EM, Siegel R, Jemal A. Cancers with increasing incidence trends in the United States: 1999 through 2008. CA Cancer J Clin [Internet]. Jan [cited 2015 Jul 22];62(2):118–28. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22281605
- Campbell SC, Novick AC, Belldegrun A, Blute ML, Chow GK, Derweesh IH, et al. Guideline for management of the clinical T1 renal mass. J Urol [Internet]. Elsevier Inc.; 2009;182(4):1271–9. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2009.07.004
- Ljungberg B, Cowan NC, Hanbury DC, Hora M, Kuczyk MA, Merseburger AS, et al. EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2010 update. Eur Urol [Internet]. 2010 Sep [cited 2015 Oct 17];58(3):398–406. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20633979
- Higgins LJ, Hong K. Renal Ablation Techniques: State of the Art. Am J Roentgenol [Internet]. 2015;(October):1–7. Available from: http://www.ajronline.org/doi/10.2214/AJR.15.14752
- Balageas P, Cornelis F, Le Bras Y, Hubrecht R, Bernhard JC, Ferrière JM, et al. Ten-year experience of percutaneous image-guided radiofrequency ablation of malignant renal tumours in high-risk patients. Eur Radiol. 2013;23(7):1925–32.
- Pandharipande P V, Gervais DA, Mueller PR, Hur C, Gazelle GS. Radiofrequency ablation versus nephron-sparing surgery for small unilateral renal cell carcinoma: cost-effectiveness analysis. Radiology [Internet]. 2008 Jul [cited 2015 Oct 26];248(1):169–78. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18458248
- Olweny EO, Park SK, Tan YK, Best SL, Trimmer C, Cadeddu J a. Radiofrequency ablation versus partial nephrectomy in patients with solitary clinical t1a renal cell carcinoma: Comparable oncologic outcomes at a minimum of 5 years of follow-up. Eur Urol. 2012;61(6):1156–61.
- Ahmed M. Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria--a 10-year update: supplement to the consensus document. J Vasc Interv Radiol [Internet]. 2014 Nov [cited 2015 Oct 29];25(11):1706–8. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25442133
- Gervais D a., Arellano RS, McGovern FJ, McDougal WS, Mueller PR. Radiofrequency ablation of renal cell carcinoma: Part 2, lessons learned with ablation of 100 tumors. Am J Roentgenol. 2005;185(1):72–80.
- Levinson AW, Su L-M, Agarwal D, Sroka M, Jarrett TW, Kavoussi LR, et al. Long-term oncological and overall outcomes of percutaneous radio frequency ablation in high risk surgical patients with a solitary small renal mass. J Urol [Internet]. 2008 Aug [cited 2015 Oct 23];180(2):499–504; discussion 504. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18550123
- Tracy CR, Raman JD, Donnally C, Trimmer CK, Cadeddu JA. Durable oncologic outcomes after radiofrequency ablation: experience from treating 243 small renal masses over 7.5 years. Cancer [Internet]. 2010 Jul 1 [cited 2015 Oct 23];116(13):3135–42. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20564644
- Faddegon S, Cadeddu J a. Does Renal Mass Ablation Provide Adequate Long-term Oncologic Control? Urol Clin North Am. 2012;39(2):181–90.
- Ferakis N, Bouropoulos C, Granitsas T, Mylona S, Poulias I. Long-term results after computed-tomography-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for small renal tumors. J Endourol [Internet]. 2010 Dec [cited 2015 Oct 23];24(12):1909–13. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20946062
- Breen DJ, Rutherford EE, Stedman B, Roy-Choudhury SH, Cast JEI, Hayes MC, et al. Management of renal tumors by image-guided radiofrequency ablation: experience in 105 tumors. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol [Internet]. Jan [cited 2015 Oct 23];30(5):936–42. Available from: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2700242&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract
- Allard CB, Coret A, Dason S, Tajzler C, Shayegan B, Matsumoto ED, et al. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for Surveillance of Radiofrequency-Ablated Renal Tumors: A Prospective, Radiologist-blinded Pilot Study. Urology [Internet]. 2015 Jun 26 [cited 2015 Oct 26]; Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/26123518
- Kong W-T, Zhang W-W, Guo H-Q, Qiu J-L, Tang M, Jiang Z-M, et al. Application of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography after radiofrequency ablation for renal cell carcinoma: is it sufficient for assessment of therapeutic response? Abdom Imaging [Internet]. 2011 Jun [cited 2015 Oct 26];36(3):342–7. Available
from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21107560
- Atwell TD, Carter RE, Schmit GD, Carr CM, Boorjian SA, Curry TB, et al. Complications following 573 percutaneous renal radiofrequency and cryoablation procedures. J Vasc Interv Radiol [Internet]. 2012 Jan [cited 2015 Oct 23];23(1):48–54. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22037491
- Rhim H, Dodd GD, Chintapalli KN, Wood BJ, Dupuy DE, Hvizda JL, et al. Radiofrequency thermal ablation of abdominal tumors: lessons learned from complications. Radiographics [Internet]. Jan [cited 2015 Oct 23];24(1):41–52. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14730035
- Del Cura JL, Zabala R, Iriarte JI, Unda M. Treatment of Renal Tumors by Percutaneous Ultrasound-Guided Radiofrequency Ablation Using a Multitined Electrode: Effectiveness and Complications. Eur Urol [Internet]. European Association of Urology; 2010;57(3):459–65. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2009.11.025
- Cutress ML, Ratan HL, Williams ST, O’Brien MF. Update on the management of T1 renal cortical tumours. BJU Int [Internet]. 2010;106(8):1130–6. Available from: