ESTUDIO POR IMAGEN DE LA NEUROPATIA DEL NERVIO PERONEO COMUN
Palabras clave:
NPC, peroneo, nervio, neuropatía, ecografíaResumen
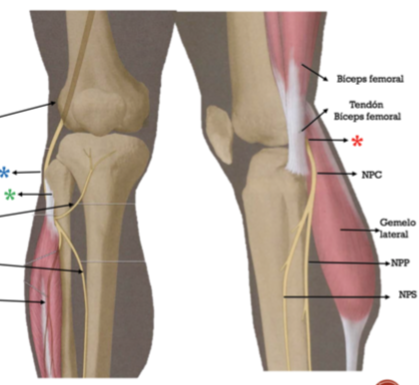
1. Describir la anatomía normal del del nervio peroneo común (NPC) y su implicación en la
patología.
2. Identificar las diferentes entidades causantes de neuropatía del NPC.
3. Utilidad de las diferentes pruebas de imagen (radiología convencional, ecografía y RM) en el diagnostico de esta patología, sus ventajas y limitaciones.
INTRODUCCIÓN:
Las neuropatías periféricas son una causa importante de dolor y limitación funcional de las extremidades. La neuropatía del nervio peroneo común (NPC) es la más frecuente de la extremidad inferior, llegando a condicionar en algunos casos dolor con deterioro importante de la calidad de vida (18).
El diagnóstico de las neuropatías periféricas suele ser un reto, ya que los pacientes suelen mostrar síntomas vagos y poco localizadores. Actualmente el diagnóstico se basa principalmente en la combinación de historia clínica detallada, exploración y estudios electrofisiológicos. Sin embargo una de las mayores dificultades es determinar la causa y lugar exacto de la lesión así como su extensión, datos que son cruciales para un correcto diagnóstico y tratamiento. La realización de pruebas de imagen como ecografía y resonancia magnética (RM) nos permiten una visualización directa del nervio y realizar el diagnóstico correcto.
Descargas
Citas
Review A. Correlation Among Ultrasound , Cross-Sectional Anatomy , and Histology of the Sciatic Nerve. 2010;35(5):442–9.
Knee PT, Donovan A, Rosenberg ZS, Conrado F. MR Imaging of Entrap- ment Neuropathies of the Lower Extremity. 2010;983–1000.
Damarey B, Demondion X, Wavreille G, Pansini V, Balbi V, Cotten a. Imaging of the nerves of the knee region. Eur J Radiol [Internet]. Elsevier Ireland Ltd; 2013 Jan [cited 2014 Oct 27];82(1):27–37. Available from: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21596499
Grant TH, Omar IM, Dumanian G a., Pomeranz CB, Lewis V a. Sonographic evaluation of common peroneal neuropathy in patients with foot drop. J Ultrasound Med [Internet]. 2015;34(4):705–11. Available from: http://www.jultrasoundmed.org//cgi/doi/10.7863/ultra.34.4.705
Alhoukail A, Panu A, Olson J, Jomha NM. Intra - articular peroneal nerve incarceration following multi - ligament knee injury. Knee Surgery, Sport Traumatol Arthrosc [Internet]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2015;23(10):3044–8. Available from: "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3626-4
Kollmer J, Bendszus M, Pham M. MR Neurography?: Diagnostic Imaging in the PNS. 2015;283–9.
Luz J, Johnson AH, Kohler MJ. Point-of-Care Ultrasonography in the Diagnosis and Management of Superficial Peroneal Nerve Entrapment?: Case Series. 2015;
Nikolopoulos D, Safos G, Sergides N, Safos P. Case Report Deep Peroneal Nerve Palsy Caused by an Extraneural Ganglion Cyst?: A Rare Case. Hindawi Publishing Corporation; 2015;2015.
Woodmass JM, Romatowski NPJ, Esposito JG, Mohtadi NGH, Longino PD. A systematic review of peroneal nerve palsy and recovery following traumatic knee dislocation. Knee Surgery, Sport Traumatol Arthrosc [Internet]. Springer Berlin Heidelberg; 2015;23(10):2992–3002. Available from: "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3676-7
Rousseau E. The anterior recurrent peroneal nerve entrapment syndrome?: A patellar tendinopathy differential diagnosis case report. Man Ther [Internet]. Elsevier Ltd; 2013;18(6):611–4. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2012.10.003
Bunch K, Hope E. Case Report An Uncommon Case of Bilateral Peroneal Nerve Palsy following Delivery?: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Hindawi Publishing Corporation; 2014;2014. 12. Vasudevan JM, Freedman MK, Beredjiklian PK, Deluca PF, Nazarian LN. Secondary to a Popliteal Lipoma?: Ultrasound Superior to Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Diagnosis. PMRJ [Internet]. Elsevier Inc.; 2011;3(3):274–9. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2010.09.014
Kili S, Perkins RDP, Hospital PR, Castle A, Tf T. Common peroneal nerve ganglion following trauma. 2004;1383:938–9.
Eleftheriou KI, Beri S, Alavi A, Tennant S. Deep peroneal nerve palsy during growth spurt?: a case report. 2014;1603–5.
Wadhwa V, Lee PP, Strome GM, Suh KJ, Carrino JA, Chhabra A. Spectrum of superficial nerve-related tumor and tumor-like lesions?: MRI features. 2015;55(3):345–58.
Kim S, Song H, Lee S. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in entrapment and compressive neuropathy — what , where , and how to see the peripheral nerves on the musculoskeletal magnetic resonance image?: part 1 . Overview and lower extremity. 2007;139–49.
Kim JY, Ihn YK, Kim JS, Chun KA, Sung MS, Cho KH. Non-traumatic peroneal nerve palsy?: MRI findings. 2007;58–64.
Wojtkiewicz DM, Saunders J, Domeshek L, Novak CB, Kaskutas V, Mackinnon SE. Social impact of peripheral nerve injuries. 2015;161–7.
Úbeda-Pérez De Heredia, Sobrá-Hidalgo G. Esguince de tobillo de primer grado como causa de paresia del nervio peroneo común. Caso clínico. Rev Andaluza Med del Deport [Internet]. Consejería de Educación, Cultura y Deporte de la Junta de Andalucía; 2015;8(2):86–91. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ramd.2014.09.002