Luces y sombras de la aplicacion de la RM funcional en la patología osteomuscular
Palabras clave:
Patología osteomuscular, póster, seramResumen
Objetivos Docentes
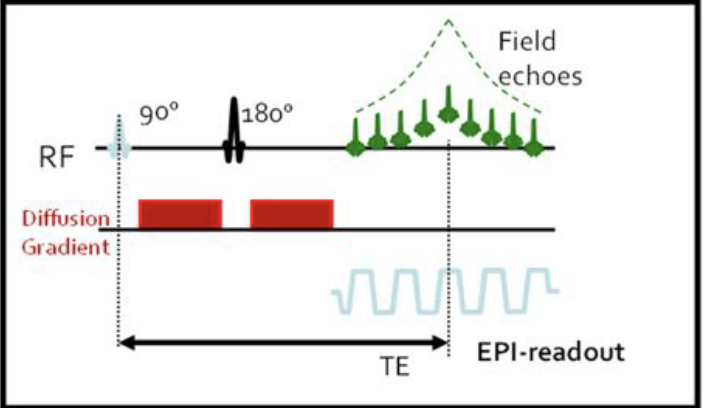
1. Definir las características de la secuencia de difusión en RM.
2. Evaluar las distintas aplicaciones de las secuencias funcionales en la patología osteomuscular.
3. Explicar los artefactos de imagen de la RM difusión para reducir-eliminar los posibles errores en el diagnóstico de imagen.
Revisión del tema
La difusión y la perfusión en RM se utiliza de forma rutinaria, desde hace años, en la neurorradiologia así como en los estudios de abdomen, pelvis y tórax. En cambio, su aplicación en el área de musculoesquelético es escasa. En la patología osteomuscular, la difusión se ha aplicado fundamentalmente en la distinción entre fracturas vertebrales patológicas y osteoporóticas, no obstante, existen otras muchas aplicaciones tanto en la patología tumoral como infecciosa.
Descargas
Citas
Luna A. et al. Diffusion MRI outside of the brain. Edit Springel. Pages 1-15.
Bley TA, Wieben O, Uhl M. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in musculoskeletal radiology: applications in trauma, tumors, and inflammation. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009;17(2):263–75.
Luna A. et al. Diffusion MRI outside of the brain. Edit Springel. Pages33-49..
Costa FM, Ferreira EC, Vianna EM..Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging for the evaluation of musculoskeletal tumors. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2011 Feb;19(1):159-80.
Luna A. et al. Diffusion MRI outside of the brain. Edit Springel. Pages 80-81. 33-49
Oka K, Yakushiji T, Sato H, Hirai T, Yamashita Y, Mizuta H. The value of diffusion-weighted imaging for monitoring the chemotherapeutic response of osteosarcoma: a comparison between average apparent diffusion coefficient and minimum apparent diffusion coefficient. Skeletal Radiol. 2010;39(2):141–6.
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM, Chenevert TL, Thoeny HC,Takahara T, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia. 2009;11(2):102–25.
Van Rijswijk, CSP, Kunz P, Hogendoorn PCW, Taminiau AHM, Doornbos J, Bloem JL. Diffusion-weighted MRI in the characterization of soft-tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2002;15 (3):302–7.
Vermoolen M.A. Kwee T. C. And J. Nievelstein R. A. Apparent diffusion coefficient measurements in the differentiation between benign and malignant lesions: a systematic review Insights Imaging (2012) 3:395–409)
Maeda M, Matsumine A, Kato H, Kusuzaki K, Maier SE, Uchida A, et al. Soft-tissue tumors evaluated by line-scan diffusionweighted imaging: influence of myxoid matrix on the apparent diffusion coefficient. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25(6):1199– 204.
Nagata S, Nishimura H, Uchida M, Sakoda J, Tonan T, Hiraoka K, et al. Diffusion-weighted imaging of soft tissue tumors: usefulness of the apparent diffusion coefficient for differential diagnosis. Radiat Med. 2008;26(5):287–95.
Kathryn M. Olsen, et al. : Tumoral Calcinosis: Pearls, Polemics, and Alternative Possibilities May-June 2006 Volume 26, Issue 3.
Oka K MD et al. Usefulness of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging for Differentiating Between Desmoid Tumors and Malignant Soft Tissue Tumors Journal of magnetic of Resonance Imaging 33: 189–193 (2011)
Ozkan Unal The diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in soft tissue abscesses. European Journal of Radiology 77 (2011) 490–494.
Harish S. et al. MR imaging of skeletal soft tissue infection: utility of diffusion-weighted imaging in detecting abscess formation. Skeletal Radiol (2011) 40:285–294 .
Oka K, Yakushiji T, Sato H, Yorimitsu S, Hayashida Y, Yamashita Y, et al. Ability of diffusion-weighted imaging for the differential diagnosis between chronic expanding hematomas and malignant soft tissue tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;28(5):1195–200.
Khoo Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) in musculoskeletal MRI: a critical review. Skeletal Radiol (2011) 40:665–681
Einarsdóttir H, Karlsson M, Wejde J, Bauer H. Diffusionweighted MRI of soft tissue tumours. Eur Radiol. 2004;14 (6):959–63.
Balliu E, Vilanova JC, Peláez I, Puig J, Remollo S, Barceló C, et al. Diagnostic value of apparent diffusion coefficients to differentiate benign from malignant vertebral bone marrow lesions. Eur J Radiol. 2009;69(3):560–6.
Raya JG, Dietrich O, Reiser MF, Baur-Melnyk A. Methods and applications of diffusion imaging of vertebral bone marrow. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;24(6):1207–20.
Andreas M. Herneth Diffusion weighted imaging of bone marrow pathologies European Journal of Radiology 55 (2005) 74–83.
Koppula et al. : Imaging of Multiple Myeloma: Usefulness of MRI and PET/CT; Semin Ultrasound, CT and MRI 34:566-577.
Herneth AM, Friedrich K, Weidekamm C, Schibany N, Krestan C, Czerny C, et al. Diffusion weighted imaging of bone marrow pathologies. Eur J Radiol. 2005;55(1):74–83.
Bozgeyik et al. : Role of Diffusion-Weighted MRI in the Detection of Early Active Sacroiliitis AJR 2008; 191:980–986.
Eustace S.: In vitro and in vivo spin echo diffusion imaging characteristics of synovial fluid: potential non-invasive differentiation of inflammatory and degenerative arthritis Skeletal Radiol (2000) 29:320–32.
J. Brett Fugitt, Necrotizing Fasciitis RadioGraphics, 24, 1472-1476.
Hayashida Y, Hirai T, Yakushiji T, Katahira K, Shimomura O, Imuta M, et al. Evaluation of diffusion-weighted imaging for the differential diagnosis of poorly contrast-enhanced and T2- prolonged bone masses: initial experience. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;23(3):377–82.
Dudeck O, Zeile M, Pink D, Pech M, Tunn P, Reichardt P, et al. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging allows monitoring of anticancer treatment effects in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2008;27(5):1109–13.
Reischauer C, Froehlich JM, Koh D, Graf N, Padevit C, JohnH, et al. Bone metastases from prostate cancer: assessing treatment response by using diffusion-weighted imaging and functional diffusion maps– initial observations. Radiology. 2010;257(2):523–31.
Fischer MA, Nanz D, Hany T, Reiner CS, Stolzmann P, Donati OF, et al. Diagnostic accuracy of whole-body MRI/DWI image fusion for detection of malignant tumours: a comparison with PET/CT. Eur Radiol [Epub ahead of print]. doi:10.1007/s00330- 010-1929-x 16.
Kwee TC, Takahara T, Ochiai R, Katahira K, Van Cauteren M, Imai Y, et al. Whole-body diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Eur J Radiol. 2009;70(3):409–17.
Daldrup-Link HE, Franzius C, Link TM, Laukamp D, Sciuk J, Jürgens H, et al. Whole-body MR imaging for detection of bone metastases in children and young adults: comparison with skeletal scintigraphy and FDG PET. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2001;177 (1):229–36.
Luna A. et al. Diffusion MRI outside of the Brain, pages 366-393. Ed. Springel).
Chaabra A, Charlian M, Soldatos T, Andreseisek G, Faridian-Aragh N, Williams E, Belzberg AJ, Carrino JA. 3-T high-resolution MR neurography of sciatic neuropathy. AJR 2012 Apr;198 (4):357-64.
Guggerberger R, Markovic D, Eppenberger P, Chhabra A, Schiller A, Nanz D, Prüssman K, Andreisek G. Assessment of median nerve with MR neurography by using diffusiontensor imaging:normative and pathologic diffusion values. Radiology 2012 Oct; 265 (1):194-205.
Pecthprapa CN, Rosenberg ZS, Sconfienza LM, Cavalcant CF, Vieira FL, Zember JS. MR imaging of entrapment neuropathies of lower extremity. Part1. The pelvis and hip. Radiographic