Dame fractales y mediré el mundo:
análisis fractal muscular para evaluar el síndrome de fragilidad.
Palabras clave:
análisis fractal muscular, poster, seram, síndrome de fragilidad, eco intensidad, EIResumen
OBJETIVOS
1. Determinar si la eco intensidad (EI) puede utilizarse como un biomarcador de imagen para el síndrome de fragilidad.
2. Determinar si el análisis fractal podría usarse para caracterizar la estructura muscular por ultrasonido.
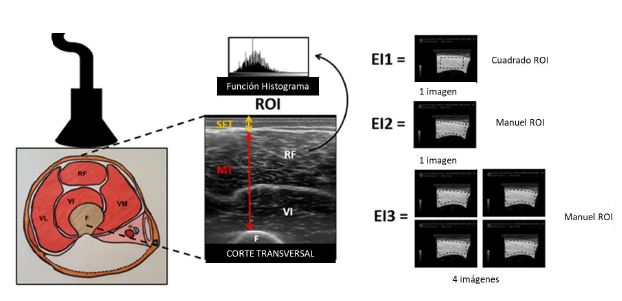
MATERIALES Y MÉTODOS
Después de la aprobación del protocolo por el comité de ética, nosotros seleccionamos las imágenes ecográficas de un estudio previo (Miron Mombiela et al 2017). El estudio previo consistió en sujetos de 60 años o mayores, hombres y mujeres, remitidos desde un centro de atención primaria, que participaron en el grupo experimental. Este grupo fue subdividido de acuerdo con el fenotipo de fragilidad (Fried et al 2001). El fenotipo de fragilidad consiste en presencia de déficits en cinco aspectos pérdida de peso involuntaria, aumento del cansancio o agotamiento, actividad física deficiente, marcha lenta y pérdida de fuerza muscular.
Los pacientes se dividieron en los siguientes grupos en función de sus respuestas a cuatro preguntas y medición de fuerza con un dinamómetro digital manual (Steiner, TL-LSC 100, Coesfeld, Germany). Por lo tanto ningún criterio fue clasificado como robusto, uno o dos criterios como pre frágil y tres o más como frágiles También tuvimos un grupo control con sujetos de 20 a 59 años de edad
De cada grupo, 12 pacientes fueron seleccionados aleatoriamente, para un total de 48 pruebas de ultrasonido muscular Se realizó un análisis de adquisición posterior a la imagen en el Departamento de Fisiología de la Universidad de Valencia (Figura 1).
Descargas
Citas
• Akima , H., Yoshiko , A., Tomita, A., Ando, R., Saito , A., Ogawa , M., . . . Tanaka, N. I. (2017). Relationship between quadriceps echo intensity and functional and morphological characteristics in older men and women . Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics , 70, 105 111. doi:10.1016/j.archger.2017.01.014
• Bartley , J. M., & Studenski , S. A. (2017). Muscle ultrasound as a link to muscle quality and frailty in the clinic . Journal of the American Geriatrics Society , doi:10.1111/jgs.15075
• Boutin , R. D., Bamrungchart , S., Bateni , C. P., Beavers , D. P., Beavers , K. M., Meehan , J. P., & Lenchik , L. (2017). CT of patients with hip fracture: Muscle size and attenuation help predict mortality . AJR. American Journal of Roentgenology , 208(6), W215. doi:10.2214/AJR.16.17226
• Bowling, A. (2009). The psychometric properties of the older people's quality of life questionnaire , compared with the CASP 19 and the WHOQOL OLD. Current Gerontology and Geriatrics Research , 2009, 298950. doi:10.1155/2009/298950 [ doi
• Caresio , C., Molinari , F., Emanuel, G., & Minetto , M. A. (2015). Muscle echo intensity : Reliability and conditioning factors . Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging , 35(5), 393 403. doi:10.1111/cpf.12175
• Fried , L. P., Tangen , C. M., Walston , J., Newman, A. B., Hirsch, C., Gottdiener , J., . . . McBurnie , M. A. (2001). Frailty in older adults : Evidence for a phenotype . The Journals of Gerontology . Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences , 56(3), 146.
• Fukumoto , Y., Ikezoe , T., Yamada , Y., Tsukagoshi , R., Nakamura, M., Mori, N., . . . Ichihashi , N. (2012). Skeletal muscle quality assessed from echo intensity is associated with muscle strength of middle aged and elderly persons . European Journal of Applied Physiology , 112(4), 1519 1525. doi:10.1007/s00421 011 2099 5
• Jenkins, N. D. M. (2016). Are resistance training mediated decreases in ultrasound echo intensity caused by changes in muscle composition , or is there an alternative explanation ? Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology , 42(12), 3050-3051. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2016.07.011
• Kerr, R. M. (2014). MRI of rectus femoris / quadriceps injury . Retrieved from http://radsource.us/rectus femoris quadriceps injury/ on the 17 of October ,
• Lipsitz , L. A. (2008). Dynamic models for the study of frailty . Mechanisms of Ageing and Development , 129(11), 675-676. doi:10.1016/j.mad.2008.09.012 [ doi
• Mirón Mombiela , R., Facal de Castro, F., Moreno, P., & Borras, C. (2017a). Ultrasonic echo intensity as a new noninvasive in vivo biomarker of frailty . Journal of the American Geriatrics Society , doi:10.1111/jgs.15002
• Mirón Mombiela , R., Facal de Castro, F., Moreno, P., & Borras, C. (2017b). Ultrasonic echo intensity as a new noninvasive in vivo biomarker of frailty . Journal of the American Geriatrics Society , doi:10.1111/jgs.15002
• Mueller , N., Murthy , S., Tainter , C., Lee, J., Riddell , K., Fintelmann , F., . . . Eikermann , M. (2016). Can sarcopenia quantified by ultrasound of the rectus femoris muscle predict adverse outcome of surgical intensive care unit patients as well as frailty ? A prospective , observational cohort study . Annals of Surgery , 264(6), 1116-1124. doi:10.1097/SLA.0000000000001546
• Pillen, S., Tak , R. O., Zwarts , M. J., Lammens , M. M., Verrijp , K. N., Arts , I. M., . . . Verrips , A. (2009). Skeletal muscle ultrasound : Correlation between fibrous tissue and echo intensity . Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology , 35(3), 443-446. doi:10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2008.09.016 [ doi
• Pillen, S., & van Alfen, N. (2011). Skeletal muscle ultrasound . Neurological Research , 33(10), 1016 1024. doi:10.1179/1743132811Y.0000000010
• Prescott, J. (2013). Quantitative imaging biomarkers: The application of advanced image processing and analysis to clinical and preclinical decision making. Journal of Digital Imaging, 26(1), 97 108. doi:10.1007/s10278 012 9465-7
• Rech, A., Radaelli, R., Goltz, F. R., da Rosa, L. H., Schneider, C. D., & Pinto, R. S. (2014). Echo intensity is negatively associated with functional capacity in older women. Age (Dordrecht, Netherlands), 36(5), 2. Epub 2014 Aug 29. doi:10.1007/s11357 014 9708 2 [doi]
• Rodriguez Mañas, L., & Fried, L. P. (2015). Frailty in the clinical scenario. Lancet (London, England), 385(9968), e9. doi:10.1016/S0140 6736(14)61595-6
• Santos, R., & Armada da Silva, P. a. S. (2017). Reproducibility of ultrasound derived muscle thickness and echo intensity for the entire quadriceps femoris muscle. Radiography (London, England: 1995), 23(3), e61. doi:10.1016/j.radi.2017.03.011
• Sullivan, D. C., Obuchowski, N. A., Kessler, L. G., Raunig, D. L., Gatsonis, C., Huang, E. P., . . . Wahl, R. L. (2015). Metrology standards for quantitative imaging biomarkers. Radiology, 277(3), 813 825. doi:10.1148/radiol.2015142202
• Sur, M. D., Namm, J. P., Hemmerich, J. A., Buschmann, M. M., Roggin, K. K., & Dale, W. (2015). Radiographic sarcopenia and self reported exhaustion independently predict NSQIP serious complications after pancreaticoduodenectomy in older adults. Annals of Surgical Oncology, 22(12), 3897-3904. doi:10.1245/s10434 015 4763 1
• Thiago Torres da Matta, Wagner Coelho de Albuquerque Pereira, Regis Radaelli, Ronei Silveira Pinto, Liliam Fernandes de Oliveira, 1U F R J P E B, . . . Brasil. (2017). Texture analysis of ultrasound images is a sensitive method to follow up muscle damage induced by eccentric exercise doi:10.1111/cpf.12441
• Ticinesi, A., Meschi, T., Narici, M. V., Lauretani, F., & Maggio, M. (2017). Muscle ultrasound and sarcopenia in older individuals: A clinical perspective. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 18(4), 290-300. doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2016.11.013
• Vanitallie, T. B. (2003). Frailty in the elderly: Contributions of sarcopenia and visceral protein depletion. Metabolism: Clinical and Experimental, 52(10 Suppl 2), 22-26.
• Walston, J., Hadley, E. C., Ferrucci, L., Guralnik, J. M., Newman, A. B., Studenski, S. A., . . . Fried, L. P. (2006). Resear ch agenda for frailty in older adults: Toward a better understanding of physiology and etiology: Summary from the american geriatrics society/national institute on aging research conference on frailty in older adults. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 54(6), 991-1001. doi:JGS745 [pii]
• Watanabe, Y., Yamada, Y., Fukumoto, Y., Ishihara, T., Yokoyama, K., Yoshida, T., . . . Kimura, M. (2013). Echo intensity obtained from ultrasonography images reflecting muscle strength in elderly men. Clinical Interventions in Aging, 8, 993-998. doi:10.2147/CIA.S47263 [doi]
• Yamada, M., Kimura, Y., Ishiyama, D., Nishio, N., Abe, Y., Kakehi, T., . . . Arai, H. (2017). Differential characteristics of skeletal muscle in community dwelling older adults. Journal of the American Medical Directors Association, 18(9), 807.e16. doi:S1525 8610(17)30278 5 [pii]
• Young, H., Southern, W. M., & Mccully, K. K. (2016). Comparisons of ultrasound estimated intramuscular fat with fitness and health indicators. Muscle & Nerve, 54(4), 743-749. doi:10.1002/mus.25105
• Zouein, F. A., Kurdi, M., Booz, G. W., & Fuseler, J. W. (2014). Applying fractal dimension and image analysis to quantify fibrotic collagen deposition and organization in the normal and hypertensive heart. Microscopy and Microanalysis: The Official Journal of Microscopy Society of America, Microbeam Analysis Society, Microscopical Society of Canada, 20(4), 1134-1144. doi:10.1017/S1431927614001044