RM-Difusión y DTI en la valoración de la patología renal.
¿Qué puede aportar?
Palabras clave:
patología renal, poster, seram, RM-Difusión, DTIResumen
Objetivos Docentes
-Recordar las bases físicas de la secuencia de difusión y tensor de difusión.
-Revisar ajustes técnicos necesarios para su aplicación en la valoración de los riñones.
-Explicar los distintos métodos de análisis de la secuencia de difusión así como la significación clínica de los parámetros derivados.
-Mostrar a través de ejemplos prácticos, los distintos escenarios clínicos en los que la difusión supone un valor añadido para la valoración de la patología renal.
Revisión del tema
1.- Introducción
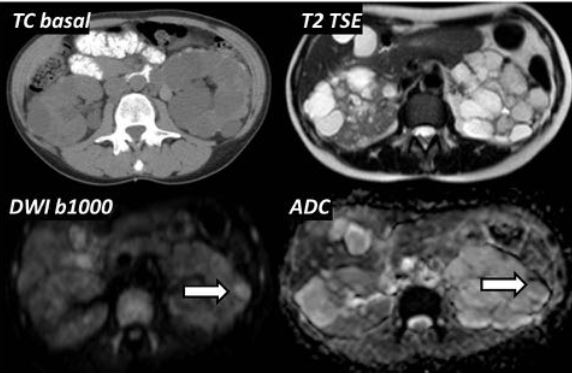
Las secuencias potenciadas en difusión (DWI) son capaces de detectar el movimiento de las moléculas de agua en un medio biológico. Dichas moléculas experimentan, en condiciones normales un desplazamiento a lo largo del espacio transcurrido un determinado periodo de tiempo. Por lo tanto, dichas secuencias no sólo permiten valorar cualitativamente dicho grado de movimiento sino también cuantificarlo aportando de esta forma información anatómica y funcional de los tejidos normales y patológicos.
Descargas
Citas
de Figueiredo EHMSG, Borgonovi AFNG, Doring TM. Basic concepts of MR imaging, diffusion MR imaging, and diffusion tensor imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am [Internet]. Elsevier Ltd; 2011 Mar [cited 2013 Jul 31];19(1):1–22.
Macarini L, Stoppino LP, Milillo P, Ciuffreda P, Fortunato F, Vinci R. Diffusion-weighted MRI with parallel imaging technique: apparent diffusion coefficient determination in normal kidneys and in nonmalignant renal diseases. Clin Imaging [Internet]. Elsevier Inc.; 2010;34(6):432–40.
Jaimes C, Darge K, Khrichenko D, Carson RH, Berman JI. Diffusion tensor imaging and tractography of the kidney in children: Feasibility and preliminary experience. Pediatr Radiol. 2014;44(1):30–41.
Wang W-J, Pui MH, Guo Y, Hu X-S, Wang H-J, Yang D. MR diffusion tensor imaging of normal kidneys. J Magn Reson Imaging [Internet]. 2014;40(5):1099–102.
Gürses B, Kiliçkesmez O, Tasdelen N, Firat Z, Gürmen N. Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney at 3 Tesla MRI: normative values and repeatability of measurements in healthy volunteers. Diagn Interv Radiol [Internet]. 2011;17(4):317–22.
Chan RW, Von Deuster C, Stoeck CT, Harmer J, Punwani S, Ramachandran N, et al. High-resolution diffusion tensor imaging of the human kidneys using a free-breathing, multi-slice, targeted field of view approach. NMR Biomed [Internet]. 2014;27(11):1300–12.
Seif M, Lu H, Boesch C, Reyes M, Vermathen P. Image registration for triggered and non-triggered DTI of the human kidney: Reduced variability of diffusion parameter estimation. J Magn Reson Imaging [Internet]. 2015;41(5):1228–35.
Notohamiprodjo M, Glaser C, Herrmann K a, Dietrich O, Attenberger UI, Reiser MF, et al. Diffusion tensor imaging of the kidney with parallel imaging: initial clinical experience. Invest Radiol [Internet]. 2008;43(10):677–85.
Kido A, Kataoka M, Yamamoto A, Nakamoto Y, Umeoka S, Koyama T, et al. Diffusion tensor MRI of the kidney at 3.0 and 1.5 Tesla. Acta radiol. 2010;51(January):1059–63.
Zhang JL, Sigmund EE, Rusinek H, Chandarana H, Storey P, Chen Q, et al. Optimization of b-value sampling for diffusion-weighted imaging of the kidney. Magn Reson Med. 2012;67:89–97.
Le Bihan D, Turner R. The capillary network: a link between IVIM and classical perfusion. Magn Reson Med. 1992;27(1):171–8.
Pentang G, Lanzman RS, Heusch P, Müller-Lutz A, Blondin D, Antoch G, et al. Diffusion kurtosis imaging of the human kidney: A feasibility study. Magn Reson Imaging [Internet]. Elsevier Inc.; 2014;32(5):413–20.
Thoeny HC, De Keyzer F, Oyen RH, Peeters RR. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in healthy volunteers and patients with parenchymal diseases: initial experience. Radiology. 2005;235(1):911–7.
Giannarini G, Petralia G, Thoeny HC. Potential and Limitations of Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Kidney, Prostate, and Bladder Cancer Including Pelvic Lymph Node Staging: A Critical Analysis of the Literature. Eur Urol [Internet]. 2012;61(2):326–40.
Chandarana H, Kang SK, Wong S, Rusinek H, Zhang JL, Arizono S, et al. Diffusion-weighted intravoxel incoherent motion imaging of renal tumors with histopathologic correlation. Invest Radiol [Internet]. 2012 Dec;47(12):688–96.
Gaudiano C, Clementi V, Busato F, Corcioni B, Ferramosca E, Mandreoli M, et al. Renal diffusion tensor imaging: Is it possible to define the tubular pathway? A case report. Magn Reson Imaging [Internet]. Elsevier Inc.; 2011;29(7):1030–3.
Zheng Z, Shi H, Zhang J, Zhang Y. Renal Water Molecular Diffusion Characteristics in Healthy Native Kidneys: Assessment with Diffusion Tensor MR Imaging. PLoS One [Internet]. 2014;9(12):e113469.
Rheinheimer S, Stieltjes B, Schneider F, Simon D, Pahernik S, Kauczor HU, et al. Investigation of renal lesions by diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging applying intravoxel incoherent motion-derived parameters--initial experience. Eur J Radiol [Internet]. Elsevier Ireland Ltd; 2012 Mar [cited 2014 Mar 2];81(3):e310–6.
Sigmund EE, Sui D, Lamparello NA, Tantillo K, Rusinek H, Babb JS, et al. and Diffusion-Tensor Imaging in Renal Tissue under Hydration and Furosemide Flow. 2012;263(3).
Huang Y, Chen X, Zhang Z, Yan L, Pan D. MRI quanti fi cation of non-Gaussian water diffusion in normal human kidney?: a diffusional kurtosis imaging study. 2014;(October):154–61.
Chan JHM, Tsui EY, Luk SH, Fung SL, Cheung YK, Chan MS, et al. MR diffusion-weighted imaging of kidney: differentiation between hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis. Clin Imaging [Internet]. 2001;25:110–3.
Xu X, Fang W, Ling H, Chai W, Chen K. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of kidneys in patients with chronic kidney disease: Initial study. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:978–83.
Zhao J, Wang ZJ, Liu M, Zhu J, Zhang X, Zhang T, et al. Assessment of renal fibrosis in chronic kidney disease using diffusion-weighted MRI. Clin Radiol [Internet]. 2014;69(11):1117–22.
Wang W, Pui MH, Guo Y, Wang L, Wang H, Liu M. 3T magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging in chronic kidney disease. Abdom Imaging [Internet]. 2014;39(4):770–5.
Lu L, Sedor JR, Gulani V, Schelling JR, O’Brien A, Flask C a., et al. Use of diffusion tensor MRI to identify early changes in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol. 2011;34(5):476–82.
Feng Q, Ma Z, Wu J, Fang W. DTI for the assessment of disease stage in patients with glomerulonephritis - correlation with renal histology. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2014;25(1):92–8.
Fan W, Ren T, Li Q, Zuo P, Long M, Mo C, et al. Assessment of renal allograft function early after transplantation with isotropic resolution diffusion tensor imaging. Eur Radiol [Internet]. 2015;
Wypych-Klunder K, Adamowicz A, Lemanowicz A, Szczesny W, Wlodarczyk Z, Serafin Z. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of transplanted kidneys: Preliminary report. Pol J Radiol [Internet]. 2014;79:94–8.
Lanzman RS, Ljimani A, Pentang G, Zgoura P, Zenginli H, Kröpil P, et al. Kidney transplant: functional assessment with diffusion-tensor MR imaging at 3T. Radiology [Internet]. 2013;266(1):218–25.
Schor-Bardach R, Alsop DC, Pedrosa I, Solazzo S a, Wang X, Marquis RP, et al. Does arterial spin-labeling MR imaging-measured tumor perfusion correlate with renal cell cancer response to antiangiogenic therapy in a mouse model? Radiology. 2009;251(3):731–42.
Taouli B, Thakur RK, Mannelli L, Babb JS, Kim S, Hecht EM, et al. Renal lesions: characterization with diffusion-weighted imaging versus contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology. 2009;251(2):398–407.
Kim S, Jain M, Harris AB, Lee VS, Babb JS, Sigmund EE, et al. T1 hyperintense renal lesions: characterization with diffusion-weighted MR imaging versus contrast-enhanced MR imaging. Radiology [Internet]. 2009;251(3):796–807.
Inci E, Hocaoglu E, Aydin S, Cimilli T. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of primary solid and cystic renal masses using the Bosniak classification. Eur J Radiol [Internet]. 2011;
Wang H, Cheng L, Zhang X, Wang D, Guo A, Gao Y, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: diffusion-weighted MR imaging for subtype differentiation at 3.0 T. Radiology [Internet]. 2010;257(1):135–43.
Sun MRM, Ngo L, Genega EM, Atkins MB, Finn ME, Rofsky NM, et al. Renal cell carcinoma: dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging for differentiation of tumor subtypes--correlation with pathologic findings. Radiology [Internet]. 2009;250(3):793–802.