INFARTO CEREBRAL AGUDO POR OCLUSIÓN CAROTÍDEA E INTRACRANEAL EN TANDEM.
TRATAMIENTO ENDOVASCULAR. EXPERIENCIA EN LOS ÚLTIMOS 5 AÑOS.
Palabras clave:
INFARTO CEREBRAL AGUDO, OCLUSIÓN CAROTÍDEA E INTRACRANEAL EN TANDEM, poster, seram, TRATAMIENTO ENDOVASCULARResumen
Objetivos
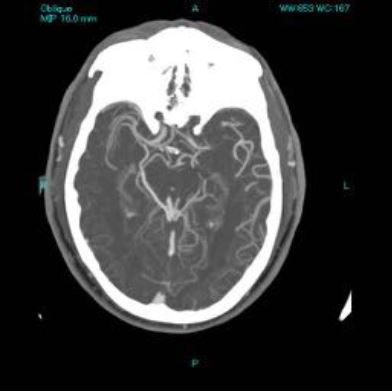
El ictus isquémico agudo resultante de la oclusión simultánea carotídea (Fig. 1, oclusión carotídea izquierda) e intracraneal tiene una historia natural con mal pronóstico.
La administración de terapia endovenosa mediante fibrinólisis (rTPA) no es suficiente para mejorar los resultados.
Revisamos nuestra experiencia en los últimos 5 años en el diagnóstico y selección de pacientes mediante imagen TC multimodal, para posterior recanalización con técnicas endovasculares.
Material y métodos
Revisamos retrospectivamente los últimos 25 pacientes con oclusión aguda extra e intracraneal simultánea o en tándem, seleccionados mediante TC-multimodal (cráneo sin contraste, perfusión cerebral y angio de troncos supraórticos y cerebral) y tratados con técnicas endovasculares (aspiración y/o stent retraíbles).
En la mayoría de pacientes realizamos angioplastia carotídea y posterior implantación de stent en fase aguda.
Descargas
Citas
Linfante I et al. Clinical and vascular outcome in internal carotid artery versus middle cerebral artery occlusions after intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 2002; 33(8):2066-2071.
Saqqur M et al. CLOTBUST Investigators. Site arterial occlusion identified by transcranial Doppler predicts the response to intravenous thrombolysis for stroke. Stroke 2007; 38(3):948-954.
Lockau H et al. Mechanical thrombectomy in tandem occlusion: procedural considerations and clinical results. Neuroradiology 2015; 57(6):589-598.
Aguilar M et al. Intracranial thrombectomy using the Solitaire stent: a historical vignette. J Neurointerv Surg 2012; 4(6):e32.
Heck DV et al. Carotid stenting and intracranial thrombectomy for treatment of acute stroke due to tandem occlusions with aggressive antiplatelet therapy may be associated with a high incidence of intracranial hemorrhage. J Neurointervent Surg 2014;0:1-6.
Hauck EF et al. Emergent endovascular recanalization for cervical internal carotid artery occlusion in patients presenting with acute stroke. Neurosurgery 2011;69(4):899-907.
Dababneh H et al. Endovascular treatment of tandem internal carotid and middle cerebral artery occlusions. J Vasc and Interv Neurology 2014;14:25-30
Jovin TG et al. Emergent stenting of extracranial internal carotid artery occlusion in acute stroke has a high revascularization rate. Stroke 2005;36(11):2426-2430
Matsubara N et al. Endovascular intervention for acute cervical carotid artery occlusion. Acta Neurochir 2013;155(6):1115-1123
Stampfl S el at. Emergency cervical internal carotid artery stenting in combination with intracranial thrombectomy in acute stroke. AJNR 2014;35(4):741-746
Fischer U et al. Endovascular therapy in 201 patients with acute symptomatic occlusion of the internal carotid artery. Eur J Neurol 2013;20(7):1017-1024
Spiotta AM et al. Proximal to distal approach in the treatment of tandem occlusions causing an acute stroke. J Neurointerv Surg 2014;21