CARCINOMATOSIS PERITONEAL DE ORIGEN OVARICA – una entidad bien conocida, estudiada con nuevas técnicas radiológicas
Palabras clave:
CARCINOMATOSIS PERITONEAL, poster, seram, ORIGEN OVARICAResumen
Objetivos Docentes
- Describir las características radiológicas de la carcinomatosis peritoneal de origen ovárico, resaltando el papel del radiólogo de cara a la planificación del tratamiento quirúrgico.
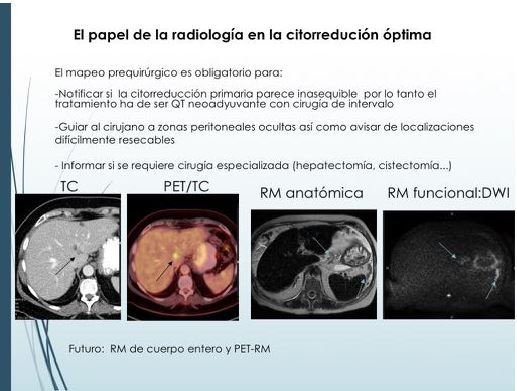
- Revisar la utilidad de las nuevas técnicas radiológicas disponibles: Tomografía computerizada multidetector (TCMD), Resonancia Magnética (RM) anatómica y funcional y Tomografía por emisión de positrones-TC (PET-TC) en el estudio de la carcinomatosis peritoneal.
- Detallar cuales son los últimos avances quirúrgicos y oncológicos y explicar las peculiaridades del seguimiento radiológico de la carcinomatosis peritoneal.
Revisión del tema
El cáncer de ovario tiene la mayor mortalidad de los tumores ginecológicos malignos y se debe a sus características tumorales, ya que en la mayoría de los casos el diagnóstico se establece en estadios avanzados (III/IV), presentándose en el 70% de los casos con carcinomatosis peritoneal o con metástasis a distancia. (fig. 1)
Descargas
Citas
J. A. Ledermann et al. On behalf of the ESMO Guidelines Working Group Newly diagnosed and relapsed epithelial ovarian carcinoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up Bristow RE, Montz FJ, Lagasse LD et al (1999) Survival impact of surgical cytoreduction in stage IV epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol 72:278–287
Oza, Amit M et al. Standard chemotherapy with or without bevacizumab for women with newly diagnosed ovarian cancer (ICON7): overall survival results of a phase 3 randomised trial The Lancet Oncology, Volume 16 , Issue 8 , 928 - 936
European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer-Gynaecological Cancer Group; NCIC Clinical Trials Group Neoadjuvant chemotherapy or primary surgery in stage IIIC or IV ovarian cancer. N Engl J Med. 2010; 363: 943–953
Johannes Grueneisen et al. Diagnostic Value of Diffusion-Weighted Imaging in Simultaneous 18F-FDG PET/MR Imaging for Whole-Body Staging of Women with Pelvic Malignancies J Nucl Med 2014 55:1930-1935 published ahead of print November 13, 2014(10.2967/jnumed.114.146886
Stephanie Nougaret, Helen C. Addley, Pierre Emmanuel Colombo, Shinya Fujii, Shaza S. Al Sharif, Sree Harsha Tirumani, Kris Jardon, Evis Sala, and Caroline Reinhold, Ovarian Carcinomatosis: How the Radiologist Can Help Plan the Surgical Approach, RadioGraphics 2012 32:6, 1775-1800
Stephanie Nougaret, Sree Harsha Tirumani, Helen Addley, Himanshu Pandey, Evis Sala, and Caroline Reinhold, Pearls and Pitfalls in MRI of Gynecologic Malignancy With Diffusion-Weighted Technique, , American Journal of Roentgenology. 2013;200: 261-276. 10.2214/AJR.12.9713
Oguz Akin, Evis Sala, Chaya S. Moskowitz, Nicole Ishill, Robert A. Soslow, Dennis S. Chi, and Hedvig HricakPerihepatic Metastases from Ovarian Cancer: Sensitivity and Specificity of CT for the Detection of Metastases with and Those without Liver Parenchymal Invasion Radiology 2008 248:2, 511-517
Limei Z, Yong C, Yan X, et al. Accuracy of positron emission tomography/computed tomography in the diagnosis and restaging for recurrent ovarian cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Gynecol Cancer 2013 May; 23(4):598-607.
Vargas, H.A., Burger, I.A., Goldman, D.A., et al, Volume-based quantitative FDG PET/CT metrics and their association with optimal debulking and progression-free survival in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer undergoing secondary cytoreductive surgery European Radiology Volume 25, Issue 11, 28 April 2015, Pages 3348-3353
Hongju Son, Shahid M. Khan, Jamal Rahaman, Katherine L. Cameron, Monica Prasad-Hayes, Linus Chuang, Josef Machac, Sherif Heiba, and Lale Kostakoglu, Role of FDG PET/CT in Staging of Recurrent Ovarian Cancer RadioGraphics 2011 31:2, 569-583
Yulia Lakhman, Stephanie Nougaret, Maura Miccò, Chiara Scelzo, Hebert A. Vargas, Ramon E. Sosa, Elizabeth J. Sutton, Dennis S. Chi, Hedvig Hricak, and Evis Sala, Role of MR Imaging and FDG PET/CT in Selection and Follow-up of Patients Treated with Pelvic Exenteration for Gynecologic Malignancies RadioGraphics 2015 35:4, 1295-1313