"Eppur si muove". Artefactos por movimiento en TC.
Conocerlos y evitarlos.
Palabras clave:
Artefactos por movimiento, poster, seramResumen
Objetivos Docentes
Revisar los artefactos en tomografía computarizada (TC) causados por movimientos del paciente o de sus estructuras anatómicas internas.
Describir su apariencia, causa, y cómo evitarlos o confundirlos con hallazgos patológicos.
Revisión del tema
INTRODUCCIÓN
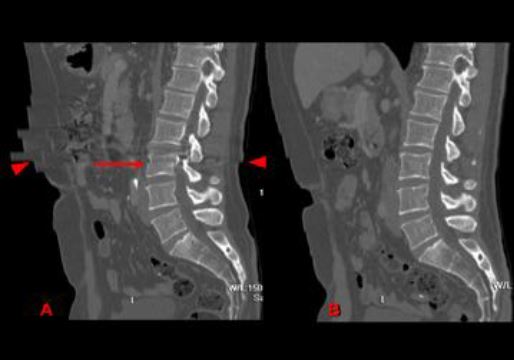
La tomografía computarizada (TC) tiene un papel muy importante en el diagnóstico por imagen, más aún desde el desarrollo de la TC multicorte o multidetector (TCMC o TCMD), que permite obtener imágenes con gran resolución espacial (con vóxeles submilimétricos isotrópicos) y temporal (con tiempos de rotación del tubo de 0,5 segundos o incluso menores).
Gracias a estas características se pueden valorar estructuras con gran detalle anatómico y/o en movimiento.
Descargas
Citas
Artigas JM et al. Multidetector CT Angiography for Acute Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Technique and Findings. RadioGraphics 2013;33:14531470.
Artul S, Yamini A. Motion artefact in multidetector CT in a child with severe chest injury resembling serious pathology. Emerg Med J 2014;31:744.
Dhandapani S, Salunke P, Mukherjee KK. ‘‘Artifactual fracturesubluxation’’ of cervical spine in computed tomography screening sans plain radiographs. The Spine Journal 2013;13:e45e48.
FarshadAmacker NA, Alkadhi H, Leschka S, Frauenfelder T. Effect of HighPitch DualSource CT to Compensate Motion Artifacts: A Phantom Study. Acad Radiol 2013; 20:12341239.
Goldberg HI. Evaluation of Ultrafast CT Scanning of the Adult Abdomen. Invest Radiol 1989;24:537543.
Huang TC, Wang YC, Chiou YR, Kao CH (2014) Respiratory Motion Reduction in PET/CT Using Abdominal Compression for Lung Cancer Patients. PLoS ONE 9(5): e98033. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098033
Ibrahim ESH, Cernigliaro JG, Pooley RA, Williams JC, Haley WE. Motion artifacts in kidney stone imaging using singlesource and dualsource dualenergy CT scanners: a phantom study. Abdom Imaging 2015;40:31613167.
Killoran et al. Motion artifacts occurring at the lung/diaphragm interface using 4D CT attenuation correction of 4D PET scans. Journal of Applied Clinical Medical Physics 2011;12(4):261274.
Mayo JR, Müller NL, Henkelman RM. The DoubleFissure Sign: A Motion Artifact on ThinSection CT Scans. Radiology 1987; 165:580581.
Ritchie CJ et al. Minimum Scan Speeds for Suppression of Motion Artifacts in CT. Radiology 1992; 185:3742.
Ritchie CJ et al. Correction of Computed Tomography Motion Artifacts Using PixelSpecific BackProjection. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging 1996;15(3):333342.
Sartoria P et al. Artefactos y artificios frecuentes en tomografía computada y resonancia magnética. Rev Argent Radiol. 2015;79(4):192204
Tarver RD, Conces DJ, Godwin JD. Motion Artifacts on CT Simulate Bronchiectasis. AJR 1988;151:11171119.
Yamamoto T, Langner U, Loo BW, Shen J, Keall PJ. Retrospective analysis of artifacts in fourdimensional CT images of 50 abdominal and thoracic radiotherapy patients. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2008;72(4):12501258.