VALOR DE LA PET-RM EN EL CANCER DE OVARIO
Palabras clave:
CANCER DE OVARIO, poster, seramResumen
Objetivos Docentes
Describir la utilidad de la imagen PET-RM tanto en el diagnóstico, estadificación pre-quirúrgica como en la detección de recidiva en cáncer de ovario
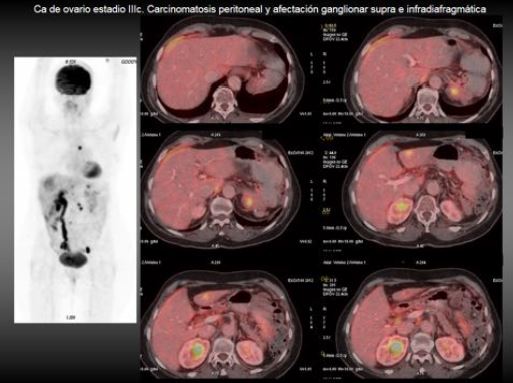
Exponer el rendimiento de ambas técnicas en la detección de recidivas, en especial ante elevación de marcadores séricos, de la carcinomatosis peritoneal y en la valoración de la respuesta al tratamiento
Revisión del tema
El cáncer de ovario es la segunda neoplasia del aparato genital femenino en frecuencia, tras el cáncer de endometrio. Sin embargo es la principal causa de mortalidad por cáncer ginecológico. En España se diagnostican unos 3.300 casos de cáncer de ovario al año, lo que supone el 5% del total de los tumores en la mujer. La incidencia ha ido aumentando lentamente desde los años 60.
Se diferencian 3 tipos de cáncer de ovario en función del tejido celular en el que se origina el cáncer: carcinoma epitelial, tumores de células germinales y tumores del estroma.
Descargas
Citas
-Imaging biomarkers in ovarian cancer: the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT. Mapelli P, Incerti E, Fallanca F, Gianolli L, Picchio M. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016 Feb 9.
-Metabolic tumor burden predicts prognosis of ovarian cancer patients who receive platinum-based adjuvant chemotherapy. Yamamoto M, Tujikawa T, Fujita Y, Chino Y, Kurokawa T, Kiyono Y, Okazawa H, Yoshida Y. Cancer Sci. 2016 Jan 20.
-Diagnostic performance of 18F-FDG PET/contrast-enhanced CT versus contrast-enhanced CT alone for post-treatment detection of ovarian malignancy. Tawakol A, Abdelhafez YG, Osama A, Hamada E, El Refaei S. Nucl Med Commun. 2016 Jan 7
-Prognostic value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT volumetric parameters in recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Mayoral M, Fernandez-Martinez A, Vidal L, Fuster D, Aya F, Pavia J, Pons F, Lomeña F, Paredes P. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2016 Mar-Apr;35(2):88-95
-(18)F-FDG-PET/CT can identify histopathological non-responders to platinum-based neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer. Vallius T, Peter A, Auranen A, Carpén O, Kemppainen J, Matomäki J, Oksa S, Roering P, Seppänen M, Grénman S, Hynninen J. Gynecol Oncol. 2016 Jan;140(1):29-35
-Predictive value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in restaging patients affected by ovarian carcinoma: a multicentre study. Caobelli F, Alongi P, Evangelista L, Picchio M, Saladini G, Rensi M, Geatti O, Castello A, Laghai I, Popescu CE, Dolci C, Crivellaro C, Seghezzi S, Kirienko M, De Biasi V, Cocciolillo F, Quartuccio N; Young AIMN Working Group. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016 Mar;43(3):404-13
-Clinical and Survival Impact of FDG PET in Patients with Suspicion of Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: A 6-Year Follow-Up. Rusu D, Carlier T, Colombié M, Goulon D, Fleury V, Rousseau N, Berton-Rigaud D, Jaffre I, Kraeber-Bodéré F, Campion L, Rousseau C. Front Med (Lausanne). 2015 Jul 22;2:46
-Utility of PET/CT in the diagnosis of recurrent ovarian cancer depending on CA 125 serum level. Fularz M, Adamiak P, Czepczynski R, Jarzabek-Bielecka G, Rewers A, Kedzia W, Ruchala M.
Nuklearmedizin. 2015;54(4):158-62
-Benefits of fluorine-18 fludeoxyglucose positron emission tomography in secondary cytoreductive surgery for patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer. Peng P, Zhu ZH, Zhong ZJ, Zheng K, Yang JX, Cao DY, Shen K. Br J Radiol. 2015 Aug;88(1052)
Volume-based quantitative FDG PET/CT metrics and their association with optimal debulking and progression-free survival in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer undergoing secondary cytoreductive surgery. Vargas HA, Burger IA, Goldman DA, Miccò M, Sosa RE, Weber W, Chi DS, Hricak H, Sala E. Eur Radiol. 2015 Nov;25(11):3348-5
-Peritoneal carcinomatosis in primary ovarian cancer staging: comparison between MDCT, MRI, and 18F-FDG PET/CT. Schmidt S, Meuli RA, Achtari C, Prior JO. Clin Nucl Med. 2015 May;40(5):371-7
-Value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the Detection of Ovarian Malignancy. Park T, Lee S, Park S, Lee E, Pahk K, Rhee S, Cho J, Kim C, Eo JS, Choe JG, Kim S. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Mar;49(1):42-51
-The usefulness of 18F-FDG-PET/CT in discriminating benign from malignant ovarian teratomas. Yokoyama T, Takehara K, Yamamoto Y, Okame S, Shiroyama Y, Yokoyama T, Nogawa T, Sugawara Y. Int J Clin Oncol. 2015 Oct;20(5):960-6
-Quantitative metabolic parameters measured on F-18 FDG PET/CT predict survival after relapse in patients with relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer. Kim CY, Jeong SY, Chong GO, Son SH, Jung JH, Kim DH, Lee SW, Ahn BC, Lee J. Gynecol Oncol. 2015 Mar;136(3):498-504
-The performance of contrast-enhanced FDG PET/CT for the differential diagnosis of unexpected ovarian mass lesions in patients with nongynecologic cancer. Lee JW, Lee JH, Cho A, Yun M, Lee JD, Kim YT, Kang WJ. Clin Nucl Med. 2015 Feb;40(2):97-102
-[(18)F]FDG PET/MRI vs. PET/CT for whole-body staging in patients with recurrent malignancies of the female pelvis: initial results. Beiderwellen K, Grueneisen J, Ruhlmann V, Buderath P, Aktas B, Heusch P, Kraff O, Forsting M, Lauenstein TC, Umutlu L. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Jan;42(1):56-65.
-Maximum standardized uptake value of fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography is a prognostic factor in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma. Konishi H, Takehara K, Kojima A, Okame S, Yamamoto Y, Shiroyama Y, Yokoyama T, Nogawa T, Sugawara Y. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 2014 Sep;24(7):1190-4