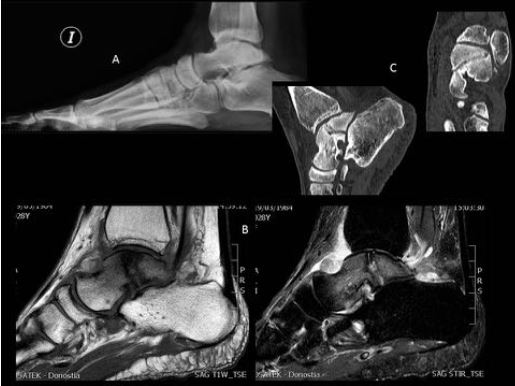
diagnostico por imagen de las fracturas de estrés
Palabras clave:
fracturas de estrés, poster, seramResumen
Objetivos Docentes
Describir los hallazgos radiológicos de las fracturas de estrés en las diferentes técnicas de imagen (radiografía simple, TC y RM).
Demostrar estos hallazgos en diferentes casos y localizaciones.
Revisión del tema
Las fracturas de estrés se pueden clasificar principalmente en 2 grupos:
- Por insuficiencia: hueso debilitado por otras patologías como pueden ser la osteoporosis (suelen localizarse en el sacro, las ramas púbicas y las extremidades inferiores), artritis reumatoidea, diabetes mellitus u otros factores como el uso de esteroides o antecedentes de radioterapia.
- Por fatiga: estímulos repetidos en un hueso sano, son más frecuentes de pacientes jóvenes y deportistas y su localización se asocia a la actividad realizada.
Descargas
Citas
Berger FH, Jonge MC, Maas M. Stress fractures in the lower extremity. The importance of increasing awareness amongst radiologist. Eur J Radiol. 2007; 62: 16-26
Peris P. Stress fractures. Best Pract Res Cl Rh. 2003; 17: 1043-61.
Kiuru Mj, Pihlajamaki HK, Hietanen HJ. MR imaging, bone scintigraphy, and radiography in bone stress injuries of the pelvis and the lower extremity. Acta Radiol 2002; 43: 207-12
Lassus J, Tulikoura I, Konttinen YT, et al. Bone stress injuries of the lower extremty: a review. Acta Orthop Scand 2002; 73: 359-68
S Y LIONG, MRCS, FRCR and R W WHITEHOUSE, MD, FRCR. Lower extremity and pelvic stress fractures in athletes. The British Journal of Radiology, 85 (2012), 1148–1156.
Krestan C, Hojreh A. Imaging of insufficiency fractures. Eur J Radiol. 2009 Sep;71(3):398-405.
Moran DS, Evans RK, Hadad E. Imaging of lower extremity stress fracture injuries.Sports Med. 2008;38(4):345-56.
Sanchez TR, Jadhav SP, Swischuk LE. MR imaging of pediatric trauma. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2009 Aug;17(3):439-50, v.
Kelsey JL, Bachrach LK, Procter-Gray E, et al. (2007). "Risk factors for stress fracture among young female cross-country runners". Med Sci Sports Exerc 39 (9): 1457–1463.
Datir A P. Stress-related bone injuries with emphasis on MRI. Clin Radiol. 2007; 62(9):828-36.
Spitz D J, Newberg A H. Imaging of stress fractures in the athlete. Radiol Clin North Am. 2002; 40(2):313-31.
Matheson G O, Clement D B, McKenzie D C, Taunton J E, Lloyd-Smith, Knapp T P, Garrett W E, Jr. Stress fractures: General concepts. Clin Sports Med. 1997; 16(2):339-56.
Schmid M R, Hodler J, Vienne P, Binkert C A, Zanetti M. Bone marrow abnormalities of foot and ankle: STIR versus T1-weighted contrastenhanced fat-suppressed spin-echo MR imaging. Radiology. 2002; 224(2):463-9.
Kiuru M J, Pihlajamaki H K, Ahovuo J A. Fatigue stress injuries of the pelvic bones and proximal femur; evaluation with MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2003; 13(3):605-11.
Beck TJ, Ruff CB, Shaffer RA. Stress fracture in military recruits: gender differences in muscle and bone susceptibility factors. Bone. Sep 2000;27(3):437-44.
Reeder MT, Dick BH, Atkins JK. Stress fractures. Current concepts of diagnosis and treatment. Sports Med. Sep 1996;22(3):198-212.
Loud KJ, Micheli LJ, Bristol S, Austin SB, Gordon CM. Family history predicts stress fracture in active female adolescents. Pediatrics. Aug 2007;120(2):e364-72.
Popp KL, Hughes JM, Smock AJ, Novotny SA, Stovitz SD, Koehler SM, et al. Bone geometry, strength, and muscle size in runners with a history of stress fracture. Med Sci Sports Exerc. Dec 2009;41(12):2145-50.
Markey KL. Stress fractures. Clin Sports Med. Apr 1987;6(2):405-25.
Deutsch AL, Coel MN, Mink JH. Imaging of stress injuries to bone. Radiography, scintigraphy, and MR imaging. Clin Sports Med. Apr 1997;16(2):275-90.
Arendt EA, Griffiths HJ. The use of MR imaging in the assessment and clinical management of stress reactions o fbone in high-performance athletes. Clin Sports Med.Apr 1997;16(2):291-306.
Moran DS, Evans RK, Hadad E. Imaging of lower extremity stress fracture injuries. Sports Med. 2008;38(4):345-56.
Lee JK, Yao L. Stress fractures: MR imaging. Radiology. Oct 1988;169(1):217-20.
Fredericson M, Bergman AG, Hoffman KL, Dillingham MS. Tibial stress reaction in runners. Correlation of clinical symptoms and scintigraphy with a new magnetic resonance imaging grading system. Am J Sports Med 1995; 23:472-481.
Mann JA, Pedowitz DI. Evaluation and treatment of navicular stress fractures, including nonunions, revision surgery, and persistent pain after treatment. Foot Ankle Clin. 2009;14(2):187-204.
Fredericson M, Jennings F, Beaulieu C, Matheson GO. Stress fractures in athletes. Top Magn Reson Imaging. 2006;17(5):309-325.
Matheson GO, Clement DB, McKenzie DC, Taunton JE, Lloyd-Smith DR, MacIntyre JG. Stress fractures in athletes. A study of 320 cases. Am J Sports Med. 1987;15(1):46-58.
Gaeta M, Minutoli F, Scribano E, et al. CT and MRI findings in athletes with early tibial stress injuries: comparison with bone scintigraphy and emphasis on cortical abnormalities. Radiology. 2005;235(2):553-561.
Lee CH, Huang GS, Chao KH, Jean JL, WuSS. Surgical treatment of displaced stress fractures of the femoral neck in military recruits: a report of 42 cases. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2003;123(10):527-533.
Cabarrus MC, Ambekar A, Lu Y et-al. MRI and CT of insufficiency fractures of the pelvis and the proximal femur. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;191 (4): 995-1001.
Peh WC, Khong PL, Yin Y et-al. Imaging of pelvic insufficiency fractures. Radiographics. 1996;16 (2): 335-48.
Isdale AH. Sacral insufficiency fractures: an unsuspected cause of low back pain. Rheumatology (Oxford). 1999;38 (1): 90.
Standaert CJ, Herring SA (2000). "Spondylolysis: a critical review“. British journal of sports medicine 34 (6): 415–22.
Boden BP, Osbahr DC, Jimenez C. Low-risk stress fractures. Am J Sports Med. Jan-Feb 2001;29(1):100-11.