¿Hay Acuerdo Entre Radiólogos Con La Escala ASPECTS Para Informar El Ictus?.
Palabras clave:
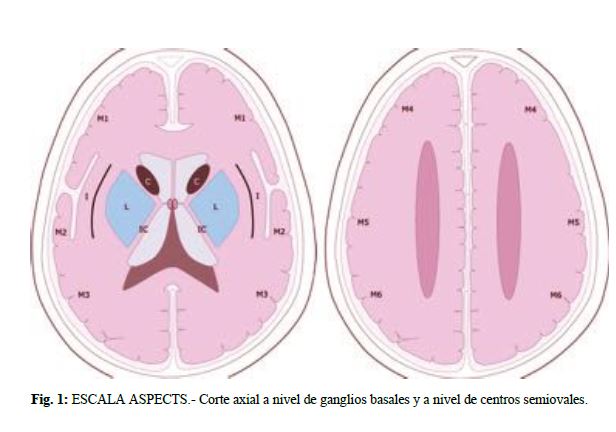
Escala ASPECTS, poster, seram, ictusResumen
Objetivos
El ictus es un trastorno brusco de la circulación cerebral que altera la función de una determinada región del cerebro.
• Causan una alta morbi-mortalidad (1ª causa en mujeres, 2ª en hombres; 1ª causa de discapacidad física y 2ª causa de demencia).
• Generan muchas exploraciones radiológicas en los servicios de urgencias en el mundo y
• Suponen grandes costes sociosanitarios ( 3-4% recursos)
El ictus es una emergencia neurológica que requiere una actuación inmediata, en las 1ª horas, para salvar tejido cerebral. Los importantes avances en las terapias de reperfusión han ido parejos con los avances en la neuroimagen por ello, se requiere un diagnóstico radiológico certero y eficaz, y también de manera eficiente, en el menor tiempo posible, que permita un manejo terapéutico inmediato del paciente.
Material y métodos
El estudio incluye 252 pacientes con ictus y estudio de imagen (TC-craneal basal) de los cuales además disponían de angio-TC craneal, interpretados por tres radiólogos (radiólogo junior, radiólogo senior de radiología urgencias y radiólogo senior en neurorradiología), que previamente realizaron un taller de consenso en lectura radiólogica del ictus.
Descargas
Citas
- Landis JR, Koch GG. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977; 33: 159-174.
- Bradley Efron. Nonparametric Estimates of Standard Error: The Jackknife, the Bootstrap and Other Methods. Biometrika Vol. 68, No. 3 (Dec., 1981), pp. 589-599.
- Lipsitz SR, Parzen M, Fitzmaurize GM, Klar N. A two-stage logistic regression model for analyzing inter-rater agreement. Psychometrika 2003; 68: 289-98.
- Feinstein A.R., Cicchetti D.V. High agreement but low kappa: I. The problem of two paradoxes, J Clin Epidemiol. 1990; 43: 543-549.
- Bland JM, Altman DG. Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1986 Feb 8;1(8476):307-10.
- Luiz RR, Leal-Costa AJ, Kale PL, Werneck GL. Assessment of agreement of a quantitative variable: a new graphical approach. J Clin Epidemiol. 2003; 56:963-7.
- Ledezma CJ, Wintermark M. Multimodal CT in stroke imaging: new concepts. Radiol Clin N Am. 2009;47:109---16.
- Marco de Lucas E, Sánchez E, Gutiérrez A, González-Mandly A, Ruiz E, Fernández-Flórez A, et al. CT protocol for acute stroke: tips and tricks for general radiologists. Radiographics. 2008;28:1673---87.
- Srinivasan A, Goyal M, Al Azri F, Lum Ch. State-ofthe-art imaging of acute stroke. Radiographics. 2006;26: S75---95.
- Tomandl BF, Klotz E, Handschu R, Stemper B, Reinhardt F, Huk WJ, et al. Comprehensive imaging of ischemic stroke with multisection CT. Radiographics. 2003;23:565---92.
- Camargo ECS, Koroshetz WJ. Neuroimaging of ischemia and infarction. NeuroRx. 2005;2:265---76.
- A. Vicente Bártulos, J.S. Martínez San Millán y M. Carreras Aja. TC multimodal en el diagnóstico del código ictus. Radiología. 2011; 53(1):16-22.
-Pexman JH, Barber PA, Hill Sevick RJ, Demchuk AM, Hudon ME, Hu WY et al. Use of the Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score (ASPECTS) for assessing CT scans in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2001 Sep;22(8):1534-42.
- Gupta AC, Schaefer PW, Chaudhry ZA, Leslie-Mazwi TM, Chandra RV, González RG, et al. Interobserver reliability of baseline noncontrast CT Alberta Stroke Program Early CT Score for intra-arterial stroke treatment selection. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2012 Jun;33(6):1046-9. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A2942. Epub 2012 Feb 9.
- SB. Coutts, AM. Demchuk, PA. Barber, WY. Hu, JE. Simon, AM. Buchanet al. Interobserver variation of ASPECTS in real time. Stroke. 2004;35(5):e103.
-Olga Finlayson, Verity John, Robert Yeung, Dar Dowlatshahi, Peter Howard, Liying Zhang, et al. Interobserver Agreement of ASPECT Score Distribution for Noncontrast CT, CT Angiography, and CT Perfusion in Acute Stroke. Stroke. 2013;44:234-36.